Manganese was discovered by Johan Gottlieb Gahn (SE) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word magnes meaning magnet, or magnesia nigri meaning black magnesia (MnO2). It is a hard, brittle, grey-white metal with a pinkish tinge. Impure forms are reactive and rust like iron in moist air. Manganese is most abundant ores are pyrolusite (MnO2), psilomelane [(Ba,H2O)2Mn5O10] and rhodochrosite (MnCO3). Pure metal is produced by mixing MnO2 with powered Al and ignited in a furnace. It's used in steel, batteries and ceramics. The steel in railroad tracks can contain as much as 1.2% manganese. It is crucial to the effectiveness of vitamin B1. The price of 99.9 % pure manganese pieces is 87.80 for 1000 g.
| Density / g dm -3 : | 7440 | (alpha, 293 K) |
| 6430 | (m.p.) | |
| Molar volume / cm 3 mol -1 : | 7.38 | (alpha, 293 K) |
| 8.54 | (m.p.) | |
| Electrical resistivity / µΩcm: | 144 | (20 °C) |
| Thermal conductivity / W m -1 K -1 : | 7.82 |
| Melting point / °C: | 1246 |
| Boiling point / °C: | 2061 |
| Heat of fusion / kJ mol -1 : | 14.4 |
| Heat of vaporization / kJ mol -1 : | 220.5 |
| Heat of atomization / kJ mol -1 : | 279.37 |
| First ionization energy / kJ mol -1 : | 717.28 |
| Second ionization energy / kJ mol -1 : | 1509.04 |
| Third ionization energy / kJ mol -1 : | 3248.49 |
| in the atmosphere / ppm: | - |
| in the Earth's crust / ppm: | 1400 |
| in the oceans / ppm: | 0.002 |
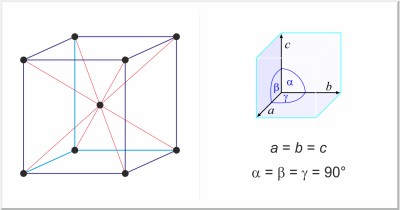
| Crystal structure: | body-centered cubic |
| Unit-cell dimensions / pm: | a=891.39 |
| Space group: | I 4 3m |

| Isotope | Relative atomic mass | Mass percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 55 Mn | 54.938050(1) | 100 |
| Balanced half-reaction | E o / V | |
|---|---|---|
| Mn IV + e - → Mn III | +1.65 | (14 mol dm -3 H2SO4) |
| Mn III + e - → Mn II | +1.59 | (14 mol dm -3 H2SO4) |
| Mn 3+ + e - → Mn 2+ | +1.51 | (7.5 mol dm -3 H2SO4) |
| Mn 2+ + 2e - → Mn (s) | - 1.180 | |
| MnO4 - + e - → MnO4 2- | +0.564 | |
| MnO4 - + 2H2O + 3e - → MnO2 (s) + 4OH - | +0.588 | |
| MnO4 - + 4H + + 3e - → MnO2 (s) (alpha) + 2H2O | +1.695 | |
| MnO4 - + 4H + + 3e - → MnO2 (s) (beta) + 2H2O | +1.679 | |
| MnO4 - + 8H + + 4e - → Mn 3+ + 4H2O | +1.506 | |
| MnO4 - + 8H + + 5e - → Mn 2+ + 4H2O | +1.51 | |
| MnO4 2- + 4H + + 2e - → MnO2 (s) + 2H2O | +2.257 | |
| MnO4 2- + 5H + + 2e - → HMnO2 - + 2H2O | +1.234 | |
| MnO4 2- + 2H2O + 2e - → MnO2 (s) + 4OH - | +0.51 | (18 °C) |
| MnO2 (s) + 4H + + e - → Mn 3+ + 2H2O | +0.948 | |
| MnO2 (s) (alpha) + 4H + + 2e - → Mn 2+ + 2H2O | +1.23 | |
| MnO2 (s) (beta) + 4H + + 2e - → Mn 2+ + 2H2O | +1.22 | |
| MnO2 (s) (gamma) + 4H + + 2e - → Mn 2+ + 2H2O | +0.21 | |
| Mn(OH)3 (s) + e - → Mn(OH)2 (s) + 2OH - | +0.1 | |
| Mn(CN)6 3- + e - → Mn(CN)6 4- | - 0.244 | |
| Mn(OH)2 (s) + 2e - → Mn (s) + 2OH - | - 1.55 | |
| HMnO2 - + 3H + + 2e - → Mn (s) + 2H2O | - 0.163 |
| 24 Chromium | ← | 25 Manganese | → | 26 Iron |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Manganese." EniG. Periodic Table of the Elements. KTF-Split, 18 Jan. 2024. Web. . .